Case Study - API automation using REST Assured
Posted By -
Avinash Shitole Date: 05/08/2019
Project Challenge:
One of the recent projects had only Selenium automation script in place to test the UI (Presentation layer). In addition to the UI, there was a need to automate the API’s testing as well. The challenge was to finalize a tool which could fulfill the below business requirements for API’s automation.
- Tool should allow integration with existing Selenium automation framework.
- Expecting to automate maximum number of test scenarios so that API automation coverage is very high.
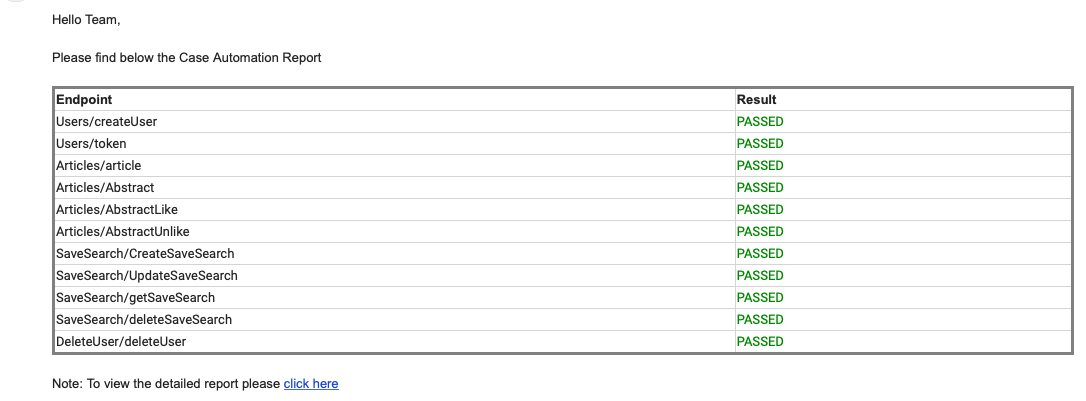
- Support for customized email report which can be shared across the team.
- Should be able to integrate the API automation suite with Jenkins
Selection of API automation tool.
Earlier we had good experience in API automation using Postman. But Postman does not support customized reports, Integration with Selenium. Also postman does not allow creating customizable http requests so it’s difficult to automate all combinations of requests. So after a thorough analysis we decided to go with REST-assured (with Maven/ TestNG) for script development. We used Maven as a build tool and Log4j for error logging.
Why Rest Assured?
Rest assured is an open-source java library which can be used to test HTTP Rest services.As we have used Postman in the past, so I would like to provide a small comparison between Postman & REST-assured.
- Rest assured allows multiple test data files whereas Postman allows only single test data file to be used in its collection.
- To generate a customise report, we can integrate TestNG with Rest Assured while in Postman, the report format is predefined.
- REST assured allows creating customizable http requests which enables us to test wide ranges of scenarios and increases the test coverage. While Postman doesn’t have that flexibility to create customizable http requests as it does not support any programming language like Java.
- Here is the link to set up Rest Assured on a local machine - Getting Started With Rest-assured
REST assured framework walkthrough

Main Packages:
-
entities package
test package
-
This package contains test scenarios & each test scenario contains multiple test cases defined using testNg. Test cases contains single/multiple endpoint calls. To confirm that endpoint is working expected we should add some assertions/verifications. There are 3 types of verifications which are listed below.
-
Status code verification: For some of the endpoints we may require to just verify the status code returned and based upon the code returned, it is determined if it passed or failed.
-
Content-Type verification: Sometimes we need to make sure that content type returned by the endpoint is matching the expected result. Depending upon the content then we mark test cases as fail or pass. Below is the code from our suite which call the GET method with path parameter & content type as JSON. Once the API call is successful then assertion is done on response to check if content type is HTML as expected.
public void Abstract() {
given(requestSpecification)
.basePath("/rendered_articles/v2")
.log().everything()
.contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.pathParam("articleId", articleId)
.get("{articleId}/abstract")
.then().assertThat().contentType(ContentType.HTML);
}
-
Schema validation: JSON Schema is a contract for your JSON document that defines the expected data types and format of each field in the response. That schema can then be used to validate that an actual JSON response from the API is compliant with the definition.
io.restassured.module.jsv.JsonSchemaValidator.matchesJsonSchemaInClasspath is a rest assured package which is used To validate the Json schema.
Below is a Json file 'Articlelist.json' with a schema definition.
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"article": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
.
.
.
"required": [
"items",
"nextPageId",
"totalCount"
]
}
Below is the code which shows that the file 'Articlelist.json' is parsed by the rest assured package io.restassured.module.jsv.JsonSchemaValidator.matchesJsonSchemaInClasspath to validate.
public void article() {
Response response = given(requestSpecification)
.param("token", user.getToken())
.get("/trending/new");
ArticlesList alist = response.then().body(matchesJsonSchemaInClasspath("articlelist.json"))
.assertThat()
.statusCode(HttpStatus.SC_OK)
.extract()
.body().as(ArticlesList.class);
}
Supported Packages:
-
helpers package:
-
This package contains classes/methods that are very often used in the framework. Some of them are like data provider helper which provides data to testNG method, property file reader, CSV file reader etc.
-
utility package:
-
This package contains small utilities which are used in a framework like - GenerateReport (generate the test report and sent it to all team members) etc.
-
customListener package:
-
TestNG provides different type of listeners that can be customized as per our requirements in the framework. In customListener package we have defined some customise functions by overwriting the existing TestNG listeners interfaces. Here is the list of interfaces which we have customized. One of the listeners inside this package is ‘TestListener’.
-
TestListener: Here methods implemented from ITestListner are used to write the test result(Pass/Fail/Skip) to external file. Later with the help of email report utility it’s used to generate the custom emailable HTML report.
-
TestNG:
-
TestNG is used for test case execution and test report generation.
-
Log4j:
-
Log4j is an open source logging framework. We have used it to capture the automation logs only in case the test cases fails.
Other supported automation tools:
-
Maven:
-
Maven as the auto-build and dependency management tool.
-
Bitbukcet:
-
Source code management tool for version control.
-
Jenkins:
-
Our Jenkins automation job used to pull the latest code from the Bitbucket repository and executes it in headless mode. We also configured the Jenkins job so that any team member can execute the script module wise as well. Obviously we made some changes in our script as well to support it.
Conclusion:
-
More flexibility with writing tests, as it is based on Java. We were able to write more complex scenarios which helped us to increase the API test coverage upto 90%.
-
It’s an open source tool so free to use without any license.
-
Easy to integrate with JUnit and TestNG frameworks.
-
Support for customizable HTML email report at the end of the script.
-
Easy integration with CI tools like Jenkins etc
.