Need for automation?
Posted By -
Avinash ShitoleDate: 08/07/2019
One of our clients requested us to setup an automation suite for their web application .We were following 2 week sprint and it was becoming difficult for us to manage regression testing along with the functional testing within a short span of 1 week. So we decided to go ahead with setting up the automation for the regression test cases.
Before jumping in to write the script , we discussed with the stakeholders and identified their expectations from this automation projects and here is the list we got.
-
Client was not interested in investing on automation tools so only open source tools were the options.
-
They wanted the automation script to be executed on all the supported browsers like Chrome, FF & Safari.
-
They wanted suite/ script to be executed daily via scheduler and also wanted to integrate the automation suite with CI/ CD pipeline(via Jenkins).
-
A Customized email automation reports should be shared with all the team members so that everyone is aware of the health of the regression suite.
Solutions proposed
After considering all the expectations and possibilities we proposed Selenium Webdrivers with Java as the language for setting up the automation. Selenium was a good choice because of the below factors.
-
Supports our frontend [React JS] & backend [Java & Scala].
-
Both Selenium & Java are open source tools, so no investment required.
-
Allows script to be executed on all our supported browsers ( Chrome, FF & Safari).
-
Can be easily integrated with Jenkins (CI/CD tools).
-
Integration with TestNG framework which was required for creating the customised email report.
In order to setup Selenium, below is the list of software/jars which are required to install on the automation server.
-
Selenium Webdriver
-
Java
-
Ant : Automation build tool
-
TestNG : Test report generation tool
-
Log4j : For error logging purpose
-
Eclipse : IDE
Setting up the automation Framework:
A testing framework is a set of guidelines or rules used for creating and designing test cases.These guidelines could include coding standards, test-data handling methods, object repositories, processes for storing test results. While setting up a new automation framework from scratch, we should first decide the 2 most important components of the framework - Type & Design patterns.
-
Types of framework : After considering pros & cons of all the types, we decided to go with Hybrid framework. We prefered Hybrid framework as it is a combination of all other frameworks and can leverage the benefits of all the others frameworks.
-
Design patterns: Design patterns are the guidelines or set of protocols used for coding. It helps to make the code robust, reusable. There are different types of design patterns that are used for setting up the project/framework e.g. Page Objects pattern, Facade pattern, Singleton pattern, etc. We decided to go with POM and it’s widely used and one of the best patterns to maintain the automation code.
-
We decided to use POM design model with page factory as it makes code reusable, maintainable, also makes code readable (as methods get more realistic names).POM basically contains 2 main layers - Test Scenarios (automation Framework) and Page Object. In addition, it has other framework supporting packages as well.
Walkthrough of our automation project structure.
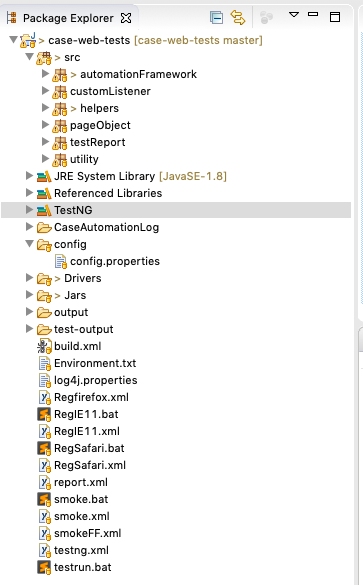
Main Packages:
-
automationFramework package(Test scenarios)
-
This package contains all the test cases. These test case calls the methods written in the page object class. It also includes the abstract test base class (TestBase.java) which contains the common methods & gets extended in all the test classes. E.g.: Driver initialization(before test or suite), Driver closing(after test or suite)
-
pageObject package
-
This package has separate class file for every single web page in the application. Each file contains web page locators and functions of the web pages. For e.g consider that we have a class file for ‘Login Page’ so this file will have all the locators from this page and the functions from this page performing some actions using the locators.
-
pageObject Package also includes the abstract page base class (PageBase.java) which gets extended in all pages where the common/custom methods used by all the pages. E.g.: Explicit wait like waitElementToBeVisible() - to wait for any element to be visible on page, waitAndClickOnElement() - to wait for the element to be clickable & click on that element etc.
Supported Packages:
-
helpers package:
-
Helpers package contains functions which uses the Selenium predefined method Or classes.Frequently used methods are generally defined in PageBase but very often used methods are added to the helpers package.Some of the examples from helpers packages are as below.
-
To switch from one browser tab to another or browser navigation (backward & forward) we have write a customized class BrowserHelper using selenium webdriver functions like driver.navigate().back() or driver.navigate().forward().
-
To execute the Javascript command like wait for the page to load created the JSHelper class which includes functions e.g. waitForPageLoaded().
-
utility package:
-
This package contains classes/utilities used in a framework like - sending email utility, APIHelper utility, etc. Here is the list of utilities we created and their descriptions.
-
APIHelper: There are few API’s which we have used in our script for new user creation (at the start of the script) and user deletion ( at the end of the script).
-
Step Recorder: This utility records the steps for test cases if it fails. At the end of the script run, the list gets added to TestNG HTML report. It helps the QA/dev team to investigate & reproduce the failing test cases effectively.
-
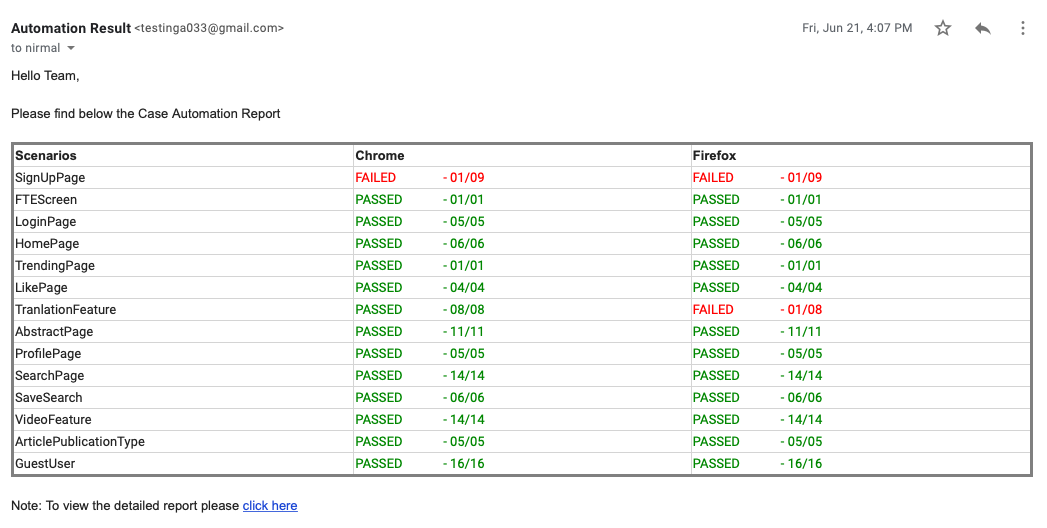
Email Report: This utility helps processing the test results from a text file ( using ITestListener interface ) and convert it into tabular HTML report which is embedded to an email and sent to the entire team. You can see one such email template below.
-
customListener package:
-
TestNG provides different type of listeners that can be customised as per our requirements in the framework. In customListener package we have defined some customized functions by overwriting the existing TestNG listeners interfaces. Here is the list of interfaces which we have customised.
-
ITestListener: Here methods implemented from ITestListner are used to write the test result(Pass/Fail/Skip) to external file. Later with the help of email report utility it’s used to generate the custom emailable HTML report.
-
IReporter: The methods implemented using IReporter links the screenshot for a failed test case in TestNG report.
-
Properties file:
-
The (.properties) file contains the static values in key-value pair to maintain project configurations data like URLs, project settings etc . Each parameter in properties file are stored as a pair of strings, in key and value format, where each key is on one line.We have used config.properties for the same.
-
TestNG:
-
TestNG is used for test case execution and test report generation.
-
Log4j:
-
Log4j is an open source logging framework. We have used it to capture the automation logs only in case the test cases fails.
Other supported automation tools:
-
Ant:
-
Ant is used as the auto build tool which is generally responsible for executing the automation script. The important component of ant is build.xml. We had 2 suites - regression and smoke test. While executing the script through ant ( via build.xml) we used to pass either smoke or regression as a parameter. Apart from suite type, there was important parameter - BrowserType which used to execute the script on the selected browsers ( Chrome, FF or Safari). Even if we need to execute the script on all browsers in parallel, then we had that option to Set the parameters in build.xml accordingly.
-
GitHub:
-
We were using GitHub repository for version control and committing our test script daily to the repository.
-
Jenkins:
-
Our Jenkins automation job used to pull the latest code from the Github repository and executes it in headless mode. We also configured the Jenkins job so that any team member can execute the script module wise as well. Obviously we made some changes in our script as well to support it.
Conclusion:
-
End to end regression of site was achieved by the automation script. Overall time in doing manual regression testing was reduced to almost 80% and we were able to use that time in testing new functionality.
-
Everyone in the team were aware of the application health as they were receiving the email HTML report daily.
-
Scalability of the script was possible due to strict design patterns followings. It was very easy to update or enhance the suite at any point of time during the application development.
-
The automation suite was grouped into two categories - smoke & regression.
-
Regression Tests: These test cases were getting executing daily at a scheduled time and everyone in the team were receiving the HTML email reports.
-
Smoke Tests: These test cases were executed only when there is new build deployment on the servers. Smoke test job on Jenkins was integrated with the build deployment job so that it gets executed at the end of the deployment by itself.It was a great achievement towards 100% build automation.